Article content
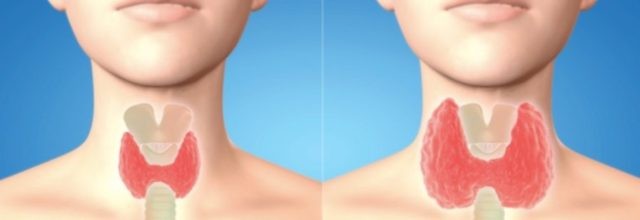
The thyroid gland affects and controls important functions and hormone production. At the same time it monitors all hormones present in the body. It regulates the function of metabolism, growth and energy production. Disease of this important organ is nowadays fairly common. It can be a decreased function (hypothyroidism) or an increased function (hyperthyroidism).
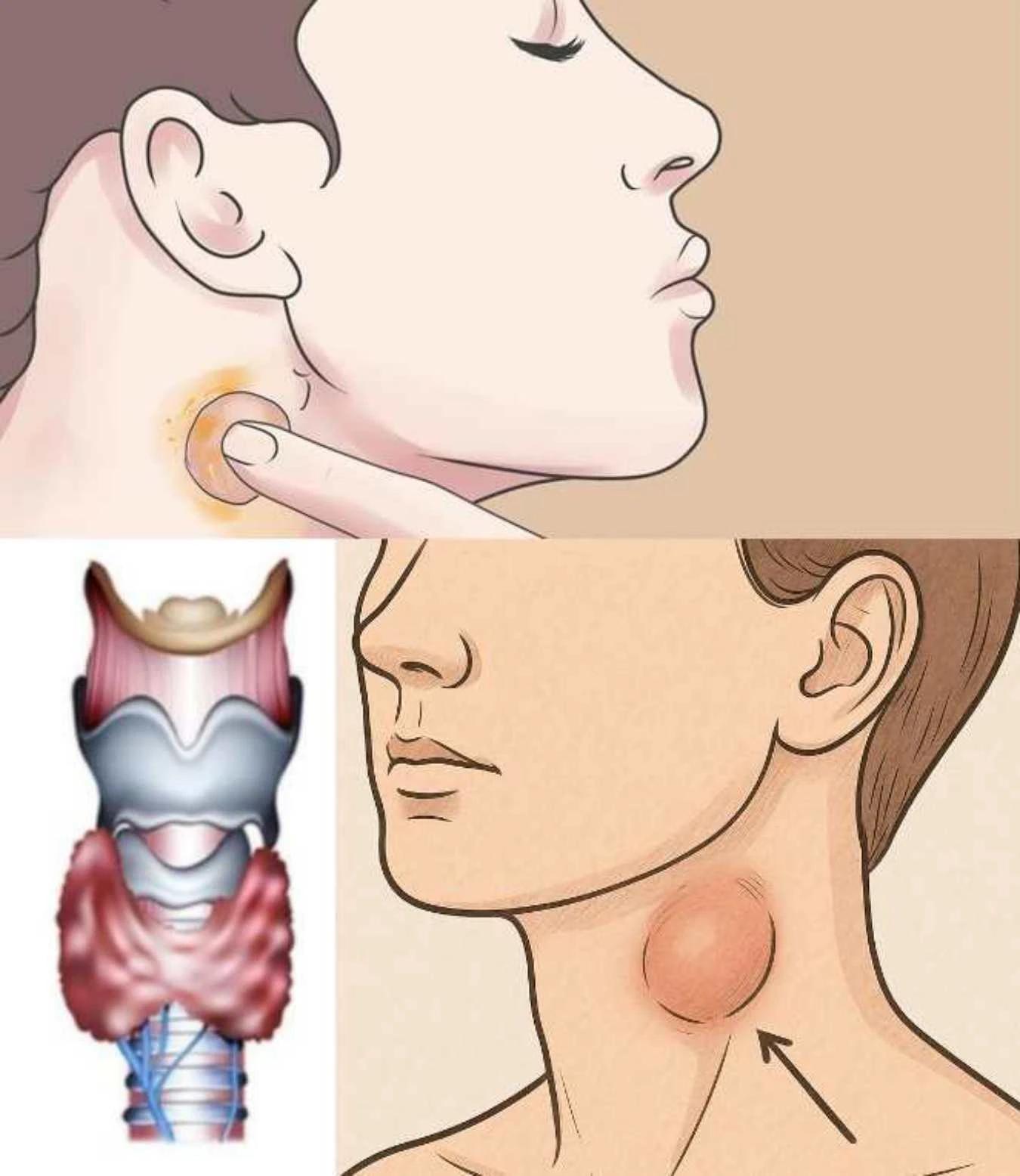
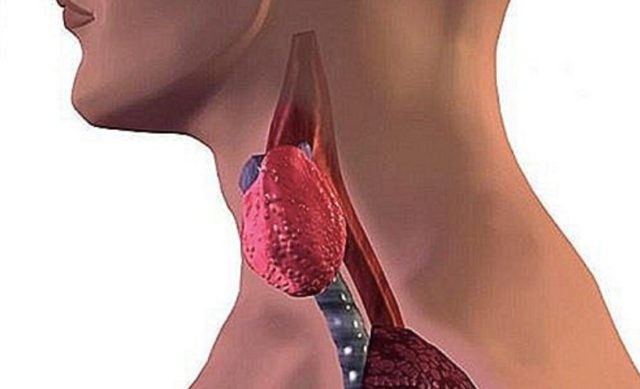
Thyroid gland
These two terms should be clearly distinguished. The symptoms of these diseases are different and the treatment itself is based on different approaches to them.
Up to 1 in 20 people suffer from a thyroid problem. Women are significantly more susceptible to this disease.
Hypothyroidism versus hyperthyroidism
These thyroid disorders are linked to an imbalance in hormone production. The production of necessary hormones should be neither too high nor too low.
Hypothyroidism
In this case it is a disease that involves reduced production of hormones.
Symptoms:
- muscle cramps
- muscle pain
- dry skin
- problems with concentration
- accumulation of fluids in the body
- hair loss and weakness
- fatigue
- sensitivity to cold
- Hyperthyroidism
Here it is the opposite situation, characterized by increased hormone production.
Symptoms:
- rapid heartbeat
- diarrhea
- anxiety
- unexpected weight loss
- sleep problems
- nervousness
- sensitivity to heat
Causes of thyroid problems
The most common cause of these thyroid problems is lifestyle itself.
- iodine deficiency
- iodine displacement by halogens (elements chemically similar to iodine – bromine, chlorine, fluorine)
- accumulation of toxins
- heavy metal burden (lead, mercury)
- chronic stress and exhaustion
Other conditions such as toxic adenomas, Graves’ disease and inflammations can also contribute to hyperthyroidism. Excessive exposure of the body to iodine, lithium or surgery on the thyroid gland itself are factors that influence this disease.
Prevention and treatment of thyroid disease
For effective prevention of these two diseases it is necessary to follow these 7 principles.
Proper nutrition
A proper diet is essential for thyroid health. Soy, sugar, processed foods, white flour and milk should be consumed in limited amounts. At the same time it is good to increase the intake of zinc, iodine, omega-3 fatty acids and selenium. These substances will support proper thyroid function.
Exercise
Regular movement and exercise support the proper functioning of the thyroid. For the thyroid to function properly, go for a walk or a bike ride.
Stress control and prevention
If you hold stress inside, you exhaust the internal secretion of the glands and thus the function of the thyroid. If your job overwhelms you or you are simply stressed for some reason, you should stop and relax. Feel free to try various stress-relief courses.
Meditation, yoga, walks, breathing exercises are an excellent choice to reduce stress. These activities relieve tension and stress, relax your body and create calm within you.
Heat therapy
Heat therapy is an excellent option for resolving thyroid problems. Try, for example, a sauna. Similar methods can detoxify the body. Toxins can limit the function of the thyroid.
Dietary supplements
Before you decide to start using supplements, consult your doctor. On store shelves you will find many products that can be purchased without a prescription.
Thyroid hormone replacement
If it is a serious case, replacement hormones can be used to help. Impressive results occur especially with T3 intake.
Prevention of problems by removing the causes of the disease
Focus on the root causes of this health problem. Thanks to this you will be able to address the problem in time and correctly.
Recap
- reduce stress
- avoid allergens and heavy metals
- eliminate nutrient deficiencies
- sleep enough
- avoid soy products
Additionally, it is good to reduce the amount of milk and gluten, which cause digestive problems and worsen the absorption of nutrients in the intestine.