Article content
A blood clot, or thrombosis, is an invisible enemy that can strike unexpectedly and become a deadly threat. Although this condition is very dangerous, it often does not receive as much attention as it deserves. While the media focus on heart disease, diabetes, or cancer, thrombosis threatens lives just as intensely, whether in young or old, men or women.
What is a blood clot?
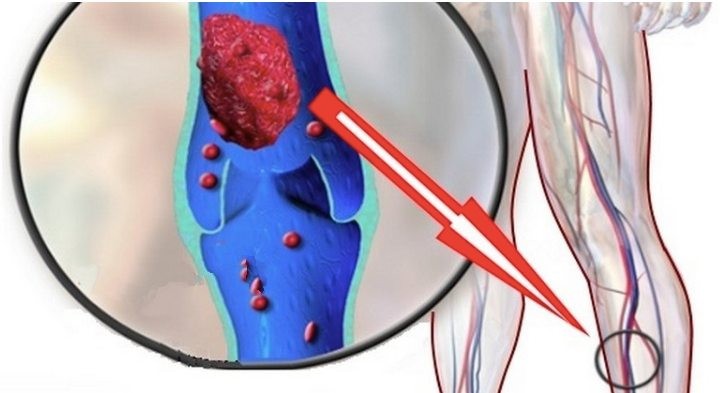
A blood clot is a condition in which clusters of red blood cells form in the veins, usually in the legs. The problem arises when this clot becomes dislodged and begins to travel through the bloodstream to other parts of the body. If it reaches the lungs, a pulmonary embolism occurs, which can be immediately fatal.
Risk groups
Each year thrombosis affects more than 2 million people worldwide, with one in ten people dying from complications related to this disease. The most at-risk include:
- Women taking hormonal contraception
- Pregnant women and women after childbirth (up to 6-8 weeks)
- People with limited mobility (e.g., hospitalized, long-distance travelers, office workers)
- Individuals with a family history of pulmonary embolisms
- People taking medications that affect blood clotting
- Older people
- Postmenopausal women
- Obese people
- Smokers
Symptoms of a blood clot
Thrombosis can strike without warning, so it is important to know its symptoms. If you notice any of the following symptoms, seek medical help:
-
Cramps in the legs or groin
Sudden cramps that cannot be explained by physical exertion may be a sign of a blood clot. -
Swelling of one or both legs
Sudden swelling and numbness of the legs, especially if you do not usually have problems with swelling, may indicate the presence of a clot. -
Chest pain or difficulty breathing
Chest pain can be a sign of a heart attack or a pulmonary embolism caused by a dislodged blood clot. In such a case, call emergency services immediately. -
Coughing up blood
This symptom is typical for pulmonary embolism and always requires immediate medical attention.
How to protect yourself from thrombosis?
If you suspect the presence of a blood clot, do not hesitate to see a doctor. There is no home remedy or herb that can cure thrombosis. A doctor can prescribe blood thinners or recommend other procedures to remove the clot.
Conclusion
Thrombosis is an insidious disease that deserves attention. Understanding the risks, recognizing the symptoms, and responding promptly can save lives. Do not underestimate the signals your body sends, and if in doubt, get checked.