Article content
A blood clot, also called thrombosis, is a silent threat that lurks in some people’s bodies and can become deadly in the blink of an eye.
Despite its enormous danger, it often remains largely unnoticed compared with other health threats and without the publicity it deserves.
The media often focus on heart disease, diabetes, cancer or obesity. However, the risk of thrombosis affects men and women equally, young and old alike.
The number of sudden deaths caused by blood clots actually exceeds the combined number of deaths from the diseases mentioned above.
What are blood clots
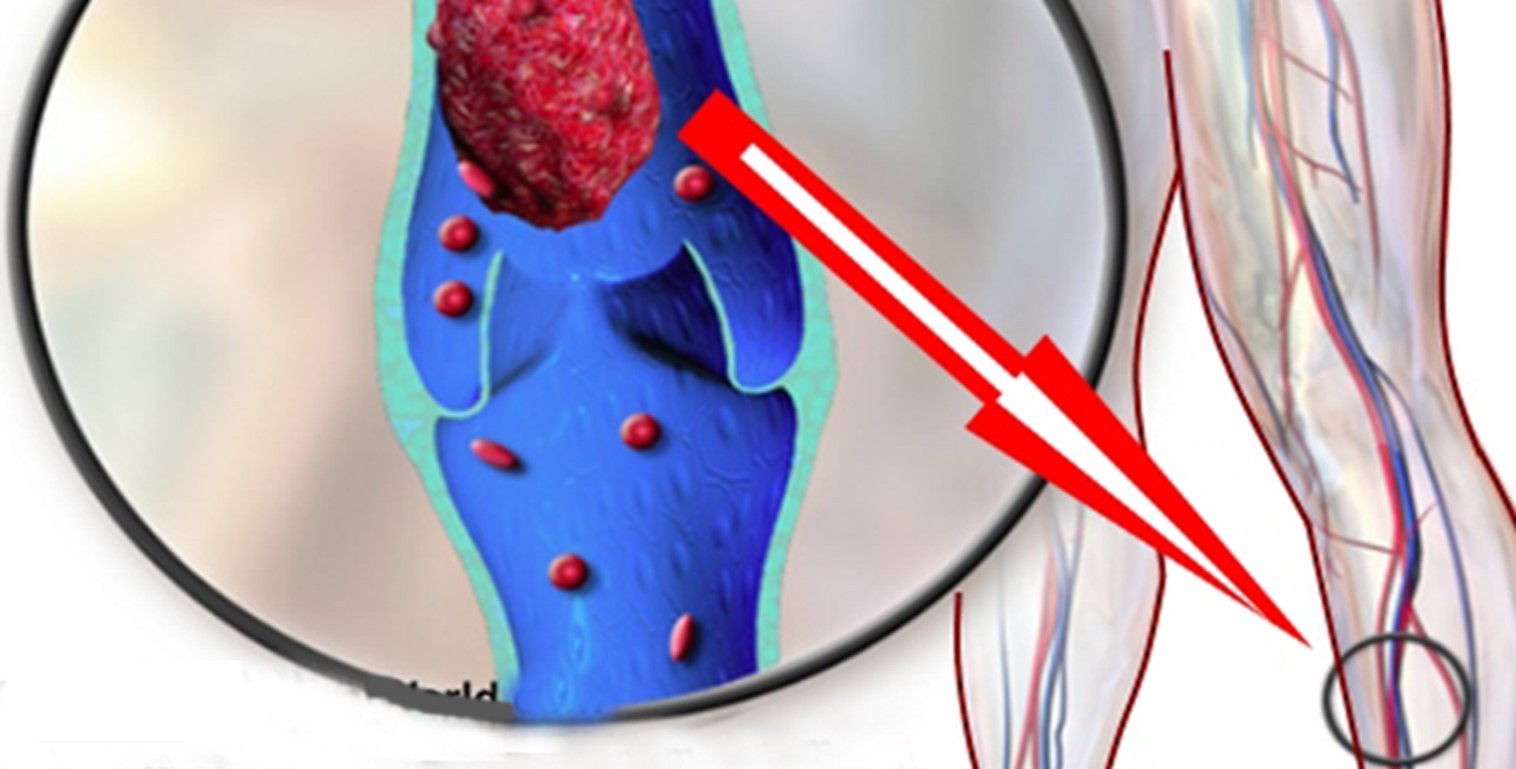
It is a medical condition in which clusters of red blood cells form in veins anywhere in the body, usually in the legs.
The danger arises when such a clot breaks free and is carried by the blood to other parts of the body. When it reaches the lungs, it is called a pulmonary embolism. That can be instantly fatal.
A blood clot manifests, for example, with swelling and pain in the affected area of the body, but there are cases when it may have no symptoms.
However, if it starts moving again and relocates to the lungs, it has the potential to quickly become life-threatening, and that without any warning.
Who has an increased risk of blood clots?
Over 2 million people worldwide are affected by thrombosis each year and most do not even realize it. Of those, one in ten people dies from complications caused by this condition.
The following groups of people are most at risk from blood clots:
- women taking hormonal contraceptives
- pregnant women and women 6 to 8 weeks after childbirth
- anyone who has limited movement for a long time (including hospitalized patients, office workers, those traveling long distances by plane, car or public transport)
- people with a family history of pulmonary embolisms
- people taking medications that affect blood clotting
- older people
- postmenopausal women
- obese people
- smokers
How to tell if you may have a blood clot in your body
Some people can develop a blood clot without belonging to any of the above risk groups. That is why it is important to know the symptoms of thrombosis.
If you notice any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical help immediately so that appropriate tests can be carried out.
Cramps in the legs or groin
If you feel sudden cramps that cannot be explained by, for example, strenuous exercise or nutritional deficiencies, the cause may be a blood clot in a vein.
This condition requires professional medical examination.
Swelling of one or both legs
As already mentioned, thrombosis most often occurs in one of the legs. Sometimes it affects both limbs at once.
If you feel sudden swelling and numbness in your legs, and your legs do not usually swell (as, for example, with diabetes or kidney disease), seek medical help. It may be a complication of thrombosis.
Chest pain or difficulty breathing
Chest pain is one of seven types of pain you should never ignore. It is also one of ten signs of an impending heart attack.
When a blood clot breaks off and travels by blood to the lungs, it can very quickly trigger a fatal pulmonary embolism.
Therefore, if you feel chest pain or have difficulty breathing, call an ambulance immediately to prevent a heart attack or pulmonary embolism.
It’s better to be wrong than to ignore it and risk death.
Coughing up blood
Another symptom of thrombosis at the stage of a pulmonary embolism is coughing up blood. This is, however, generally something that always requires medical attention.
Coughing up blood can be caused by several types of disease, but it is always important to rule out a blood clot, because unlike other cases it represents an acute threat to life.
Time always plays a crucial role in thromboses.