Article content
It is known that proteins play an important role in the functioning of our body. If you have a protein deficiency, your body will suffer.
One study says that up to approximately 1 billion people worldwide suffer from their deficiency. How do you find out if this applies to you?
The problem is that when we think about our diet we usually consider deficiencies in vitamins and minerals. However, protein content is just as important.
In our article today we will talk more about the symptoms related to their deficiency so you know when it happens to you.
1. Food cravings
If you always feel hungry or have an increased appetite, it may be due to a diet containing a low proportion of protein and a high proportion of carbohydrates and sugar.
The problem nowadays is almost unlimited access to high-calorie foods where the amount of protein is low compared to the calories.
2. Loss of muscle mass and joint pain
Muscles are the largest reservoir of protein in the body. Muscle weakness, pain and weight loss are signs of their deficiency.
Research says that this commonly occurs mainly in older people. Proteins are necessary for muscle growth and maintenance.
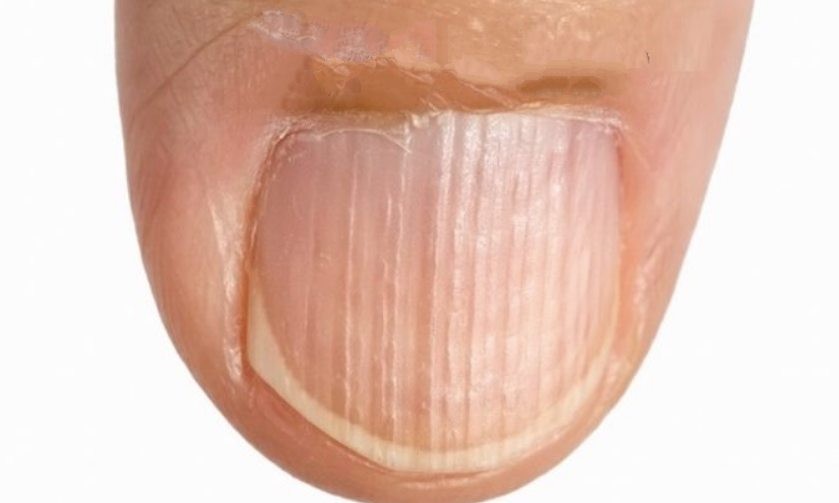
3. Skin and nail problems
Protein deficiency can lead to your nails being weak, brittle and in some cases you will observe white streaks or brownish spots on the nails.
Protein deficiency can also affect the skin because proteins enable cell regeneration, create new cells and replace dead ones.
If this happens, then you will find that your skin is dry, scaly and cracked.
4. Hair loss
Our hair is made up of 90% of a protein known as keratin. If hair does not get enough nutrients, it becomes thin and dull.
This happens because the body stops using proteins for nonessential things like hair growth in an effort to preserve other, more necessary functions.
5. Fatty liver
Fatty liver is one of the most common signs of protein deficiency.
If left untreated, it can cause more serious liver disease, trigger inflammation, scarring, or even potentially liver failure.
It is a common condition in those who consume a lot of alcohol and obese people. Today, however, it even occurs in children due to poor diet.
6. Increased risk of bone fractures
Like muscles, low protein intake can also affect bones. Protein deficiency leads to weakened bones, thereby increasing the risk of fractures.
This is mainly because “protein is necessary for the absorption of calcium and helps with bone metabolism,” as the well-known American Dr. Axe says.
7. Sleep deprivation
If you have trouble sleeping or suffer from a lack of it, it is likely related to a protein deficiency.
Dietary proteins act as building blocks for tryptophan. It is an amino acid whose low level causes sleep problems.
This means that before dinner it is good to consume protein-rich foods to achieve better sleep.
8. Brain fog
It is very important to ensure the body receives the right intake of proteins to support healthy bodily functions and especially the brain.
If you lack motivation, have poor memory or problems learning something new, it is a sign that you are likely suffering from a protein deficiency.
One study found that the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin are needed by your brain for you to be able to concentrate.
Recommended daily protein intake
The recommended minimum daily protein intake for adults is 56 g for men and 46 g for women. For children it ranges from 19 g to 34 g per day, depending on their age.
However, adequate protein intake may differ in cases where you are pregnant or ill. Then a slightly higher amount is needed.