Article content
Blood clots can have very serious consequences and some complications can be fatal.
What symptoms should we be suspicious of and what can we do about blood clots?
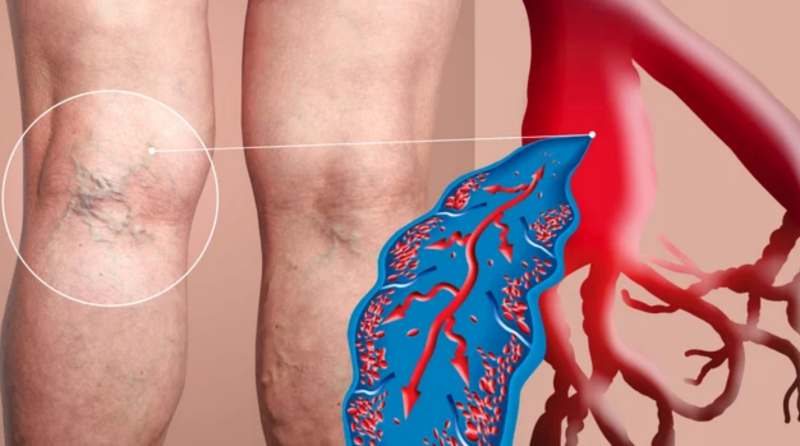
Thrombosis causes the deaths of more than a thousand people in Hungary each year. Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot gets stuck in the deep veins, typically in the legs and pelvis, but it is not uncommon for it to appear in the brain as well.
If a blood clot forms somewhere in the veins, it can be painful and very dangerous, including deep vein thrombosis. Deep vein thrombosis is like when a roadblock (blood clot) creates a huge traffic jam on the highway (blood flow), so blood and the oxygen carried by the blood cannot reach the cells. It is especially dangerous when a piece of the blood clot breaks off and reaches the pulmonary artery — in this case it causes a pulmonary embolism, which can easily be fatal. There are warning signs that indicate a blood clot somewhere in the body is blocking blood flow. If you detect them in time and see a doctor, you can prevent a tragedy.
Warning signs of a blood clot
-
Swollen leg: The most common symptom of deep vein thrombosis is swollen legs. If your legs swell in the evening, that can be normal, but sudden swelling and leg pain may signal thrombosis.
-
Pain in the arms or legs: Deep vein thrombosis is often accompanied by limb pain. Pain caused by a blood clot increases with walking or stretching the leg.
-
Red streaks on the legs: Longitudinal red lines or spots that are tender to pressure and warm to the touch may be a sign of deep vein thrombosis.
-
Chest pain: Chest pain may signal a pulmonary embolism. This pain worsens with deep inhalation and can resemble a heart attack.
-
Shortness of breath and palpitations: A blood clot in the lungs reduces the flow of oxygen, which causes a faster heartbeat and difficulty with deep breathing.
-
Persistent cough: If you cannot stop coughing and have trouble breathing, it may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. The cough may be dry or accompanied by bloody phlegm.
What to do if you have symptoms?
If you notice any of the above symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are serious conditions that require prompt medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent serious complications and save lives.
Prevention of thrombosis includes regular exercise, a healthy diet and avoiding prolonged sitting. If you have risk factors, such as a family history of thrombosis or recent surgery, consult your doctor about preventive measures.
Take care of your health and watch for warning signs so that your legs and your whole body remain in good condition!