Article content
First of all, it should be emphasized that hygienic conditions play only a minor role in the spread of tapeworms. It is important to know this because people infected with this parasite feel ashamed, although the infection is usually not caused by poor hygiene. Parasites can enter our body in the following ways:
infected meat (larvae settle in beef and pork, as well as in fish),
infected fruit and vegetables (tapeworm eggs),
contaminated water,
infected feces.
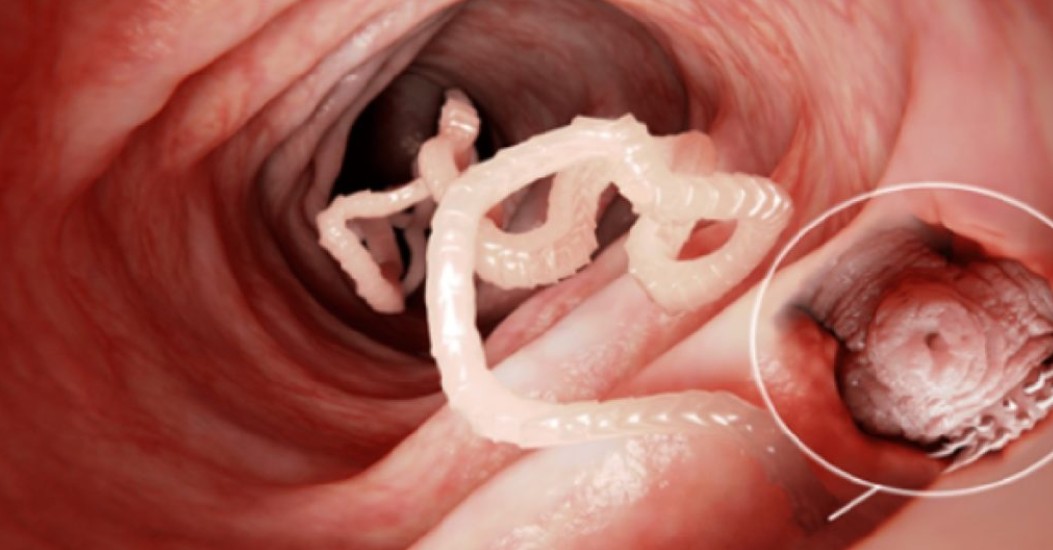
Tapeworm and its symptoms
It is quite common that the presence of a tapeworm living in the intestine is discovered only when white rice-shaped grains appear in the stool, or longer unusual formations containing parasite larvae. The reason is that the symptoms of the infection are not specific:
- digestive disorders,
- vomiting,
- diarrhea,
- abdominal pain,
- malaise,
- fatigue,
- sleep disturbances,
- malnutrition,
- weakened immunity,
- intestinal inflammation (diverticulitis)
- rarely vitamin B12 deficiency.
- An unmistakable sign is also itching of the rectum; in such a case the presence of a tapeworm can be detected by a specialist doctor through a rectal examination.
Dangerous larvae
There are also tapeworms that do not develop and do not parasitize in the small intestine, but whose larvae settle in other organs, for example in the lungs or in the brain. They can also get into the muscles and form cysts there. The following symptoms can be warning signs:
- chronic cough,
- recurrent headaches,
- cramps,
- confusion,
- epileptic seizures,
- chest pain,
- yellowing of the skin,
- pain in the liver area,
- muscle pain,
- frequent dizziness.
Identifying a tapeworm infection
The presence of a tapeworm settled in the intestines can be determined by a simple stool examination. From the collected sample, the presence of eggs or tapeworm segments in the stool is detected by microscopic methods. Diagnosing the presence of larvae is somewhat more complicated; this requires X-ray, ultrasound, or other imaging methods, or blood tests.
What are the possible complications?
In particular, the embryos (larvae) of the pig tapeworm that enter the human body cause a condition called cysticercus. In such cases, the larvae in certain organs (brain, liver, lungs, muscles, eyes, etc.) create cysts that cause inflammation. When a cyst ruptures, it can trigger dangerous allergic reactions. Parasites reaching lengths of one meter can cause blockage of the intestines, gallbladder, or pancreas. As a result, jaundice, constipation, or even appendicitis may occur. In the case of infection with cystic echinococcosis, the larvae get into the liver, which can cause enlargement of the liver or other organ damage; less commonly the lungs are affected.
Eliminating the tapeworm
The parasite is often expelled from the body by itself before its presence is detected. In other cases, we can get rid of a tapeworm using medications and dietary supplements against parasites. In rare cases surgical removal of the parasite larvae is necessary.