Article content
What are blood clots? This jelly-like mass of blood forms when the body is injured to prevent excessive bleeding.
Platelets and proteins in the plasma work together to form a clot at the injury site. After the wound heals, the body usually dissolves the clot.
However, sometimes a clot forms inside arteries or veins without an injury and does not dissolve on its own.
This can then lead to a stroke or pulmonary embolism. Clots are serious and require accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
According to the U.S. CDC:
Stroke kills more than 130,000 people in the U.S. each year – that is 1 in every 20 deaths.
In the U.S., someone has a stroke every 40 seconds. Every 4 minutes someone dies from a stroke.
Each year more than 795,000 people in the U.S. have a stroke (in Slovakia it is around 12,000 people annually). About 610,000 are first
or new strokes.
Nearly 1 in 4 are people who have previously had a stroke.
About 87% of all strokes are ischemic, where blood flow to the brain is blocked.
Strokes cost the U.S. an estimated $33 billion each year. This amount includes the costs of health care services, medications to
treat stroke and lost days at work.
Stroke is a leading cause of serious long-term disability. Stroke limits mobility in more than half of people aged 65
and older who survive a stroke.
Types of blood clots: arterial and venous
1. Arterial blood clots
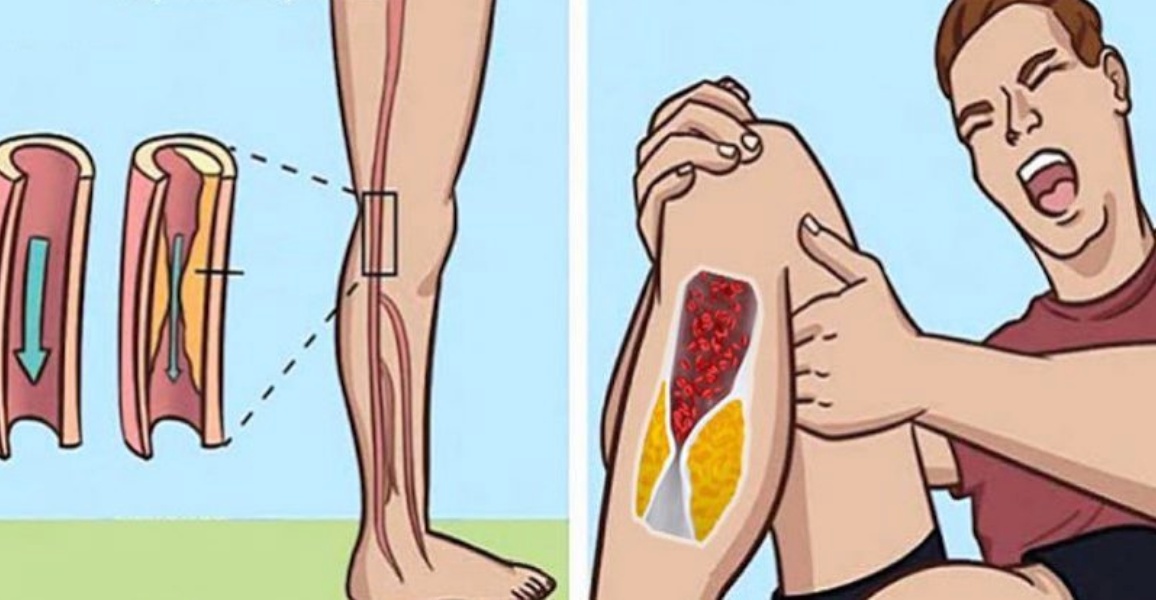
Clots can occur in arteries or in veins. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Arterial clots form in arteries and can prevent oxygen and blood from reaching vital organs. Arterial clots often form in the feet and legs; they can also occur in the brain, leading to a stroke, or in the heart, leading to a heart attack.
Symptoms of arterial clots include:
- cold hands or feet
- fingers or hands that feel cold to the touch
- loss of color in the affected area
- muscle pain or cramps in the affected area
- tingling or numbness in the leg or arm
- weakness in the affected area.
Risk factors for arterial clots that can be modified by lifestyle changes or medical treatment:
- diabetes
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol
- lack of physical activity
- obesity
- smoking
2. Venous blood clots
These clots form in the veins and tend to develop slowly. The likelihood of forming clots is higher after surgery or trauma, such as a broken leg.
There are three types of clots that form in veins: deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE) and superficial vein inflammation.
DVT – this clot usually occurs in the lower leg, thigh or pelvis, but it can also occur in other parts of the body such as the arm, brain, intestines, kidneys or liver.
PE – this is a clot that has broken off from its site of origin and can travel to the lungs. This can be fatal.
Superficial venous thrombosis – this type of clot forms in a vein near the surface of the skin. It can be painful and requires treatment.
What are the symptoms of a venous clot?
A venous clot near the surface of the skin may present these symptoms:
Red skin over the affected vein
Painful, swollen or inflamed skin over the affected vein
A vein that is tender to the touch or hard
5 primary signs and symptoms of blood clots
Symptoms of blood clots can vary depending on where in the body they are located.
According to the American Society of Hematology you may experience these 5 symptoms if a blood clot has formed in these specific areas:
1. Arm or leg – sudden or gradual pain, tenderness, swelling and warmth. Loss of hair on the legs.
2. Abdomen – severe abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea.
3. Brain – weakness of the face, arms or legs, difficulty speaking, problems with vision, sudden and severe headaches, dizziness.
4. Heart – pressure on the chest or chest pain, discomfort in other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, lightheadedness.
5. Lungs – sharp chest pain, palpitations, fever, shortness of breath, sweating and coughing up blood.
What prevents blood clots
The following are 4 natural blood-thinning remedies you need to know about:
1. Healthy eating – following a healthy diet and lifestyle is key to your overall health and the foundation for preventing blood clots.
Avoid foods that are harmful to your health, such as genetically modified and processed foods, sugar and artificial sweeteners, trans fats and refined carbohydrates.
2. Active lifestyle – regular exercise and avoiding a sedentary lifestyle are very important for your health. If you have a sedentary job, consider standing up and stretching your legs during the day.
3. Smoking – whether you smoke cigarettes or use vaping devices, tobacco products increase your risk of blood clots.
4. Medication changes – your risk of blood clots can be increased by hormonal medications, blood pressure drugs and cancer treatments. Check with your doctor whether there are any other options for you.
6 natural remedies and supplements for thinning the blood
These natural remedies and dietary supplements for thinning the blood are beneficial for your overall health and may help prevent blood clots.
1. Omega-3 fatty acids – foods rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as fish, pumpkin seeds and walnuts. You can also take them in capsule form.
2. Vitamin E – prevents oxidation. Foods rich in vitamin E include leafy green vegetables, almonds, avocado, broccoli, butternut squash and kiwi.
3. Natural antibiotics – for example garlic, olive oil and onions. There is a study showing that garlic may be useful in preventing thrombosis.
4. Vitamin C – a strong antioxidant for maintaining proper vascular health.
5. Ginkgo – reduces fibrin content, which is a protein important for clot formation.
6. Blueberries, ginger and turmeric – these foods reduce the ability of platelets to clump together, which can lead to blood clot formation.