Article content
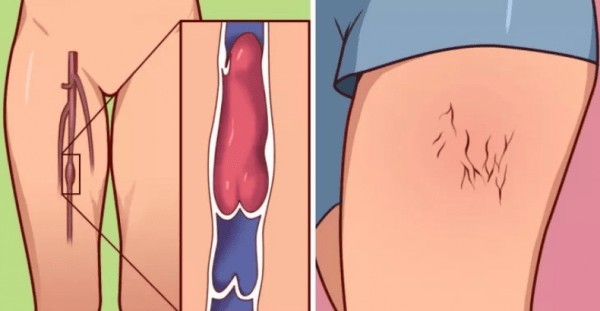
Blood clots are clumps of blood that thicken. They usually do not harm your health; on the contrary: they protect the body from bleeding. However, when blood clots appear in the veins, they can be extremely dangerous. A dangerous type of clot is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and can cause „traffic jams” in the bloodstream. If a blood clot detaches from its site and reaches the lungs or heart, it can have fatal consequences.
How does a blood clot affect your body?
If you have a blood clot in the lungs, you may feel trembling in your chest. This is caused by low oxygen levels in the lungs. As a result, your heart tries to compensate and begins to beat faster. If you find it very difficult to take a deep breath, it may be a sign of a blood clot in the lungs, called a pulmonary embolism. This can also be indicated by bouts of dry coughing, shortness of breath and chest pain. You may also cough up phlegm or blood. One of the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism is chest pain when taking a deep breath. The pain is usually sharp and stabbing. In any case you should immediately call 112, because the consequences can be fatal.
Do not ignore the symptoms, it can be a matter of minutes
Vomiting can be a sign of a blood clot in the abdomen. This condition is called mesenteric ischemia and is usually associated with severe abdominal pain. Painless loss of vision in one eye is usually a symptom of occlusion of the central retinal artery. It is considered a serious medical problem, especially if you have other symptoms such as dizziness and problems maintaining balance. Other indicators of a blood clot may include these problems:
- red or dark spots on the skin that appear for no apparent reason,
- pain in the hands or feet,
- swelling of a limb (often the ankle),
- red and warm streaks on the skin.
This is a very serious health problem that requires immediate intervention. If one or more of the above symptoms appear, call for help immediately.